Cybersecurity for the Manufacturing Industry
Mitigating Cyber Attacks with CloudConnexa
The manufacturing industry's embrace of the Internet of Things (IoT) has changed our world in countless ways — not the least of which is that it resulted in Industry 4.0. More than 250 years since the First Industrial Revolution moved from hand production methods to machines powered by steam and water power, Industry 4.0 converges new technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, robotics, 3D printing, the Internet of Things, and advanced wireless technologies.
The smart factory is at the heart of Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). These factories infuse manufacturing technologies with automation and data exchange, including the IoT, cloud computing, and cognitive computing. The benefits of 4IR include:
- Improved productivity and efficiency.
- Better agility and flexibility.
- Increased profitability and ROI.
- Improved customer experiences.
The manufacturing industry's embrace of the Internet of Things has changed our world in countless ways.
Manufacturing's digital transformation created new cyber threats, too. The extended network of connected devices — robotics, sensors, 3D printers, AI, machine learning, augmented reality (AR) — has vulnerabilities that didn’t exist on the traditional factory floor.
According to the 2021 Manufacturing Cybersecurity Threat Index, released in June 2021, one out of every five U.S. and U.K. manufacturing companies were victims of cyber crime in the previous 12 months. Almost a quarter (24%) of those reported weekly cyberattacks, making manufacturing one of the most attacked industries since the pandemic started.
Now, as the manufacturing sector attempts to overcome supply chain issues caused by the pandemic, we wanted to explore the cybersecurity risks faced and how manufacturing organizations can address security issues that come with new technologies.
Good to Know: The term industrial internet of things (IIoT) is often used interchangeably with 4IR and Manufacturing 4.0.
Manufacturing Cybersecurity Threats and Impact
Intellectual property (IP) and industrial control systems are the primary targets of cybercriminals. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a division of the U.S. Department of Commerce, reports that small and medium-sized manufacturers (SMMs) are especially susceptible to cybercrime. This is because SMMs tend to have fewer mitigation and incident response plans in place, and hackers know it. They also know these manufacturers are more likely to pay ransoms to recover IP and avoid downtime. Additional issues, beyond ransomware payouts and downtime, include:
- Information and information technology systems damage.
- Penalties and fines from regulators as well as legal fees.
- Reduced productivity.
- Information and IP loss.
- Customer relationship damage, or even customer loss.
- Reduced ability to get loans due to impacted credit.
- Income loss.
One preferred tactic of cybercriminals is ransomware attacks. A survey of Managed Service Providers (MSPs) found that Manufacturing, along with Construction, are the industries most targeted by ransomware. The same report cites ransomware as the single biggest threat to SMBs, hitting 1 in 5. And the average payment for ransomware increased 13% — to $41,198 — from Q2 2019 to Q3 2019.
Phishing emails are one of the most common ways cybercriminals gain network access. The Q3 2021 Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) Phishing Activity Trends Report found that:
- July’s 260,642 total phishing attacks was the highest in the organization’s reporting history.
- The number of phishing attacks doubled from early 2020.
- SaaS webmail was the most frequent target at 29.1% of all attacks.
- Financial institutions and payment companies accounted for 34.9% of all attacks.
- 700 brands were attacked monthly in 2021, up from 400 monthly.
All of these numbers are cause for concern, but there are cybersecurity standards and technology SMMs can use to mitigate both phishing and ransomware.
Good to Know: Manufacturers are at higher risk of USB flash drive malware infections than any other sector.
Using CloudConnexa and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework for Manufacturing Cybersecurity
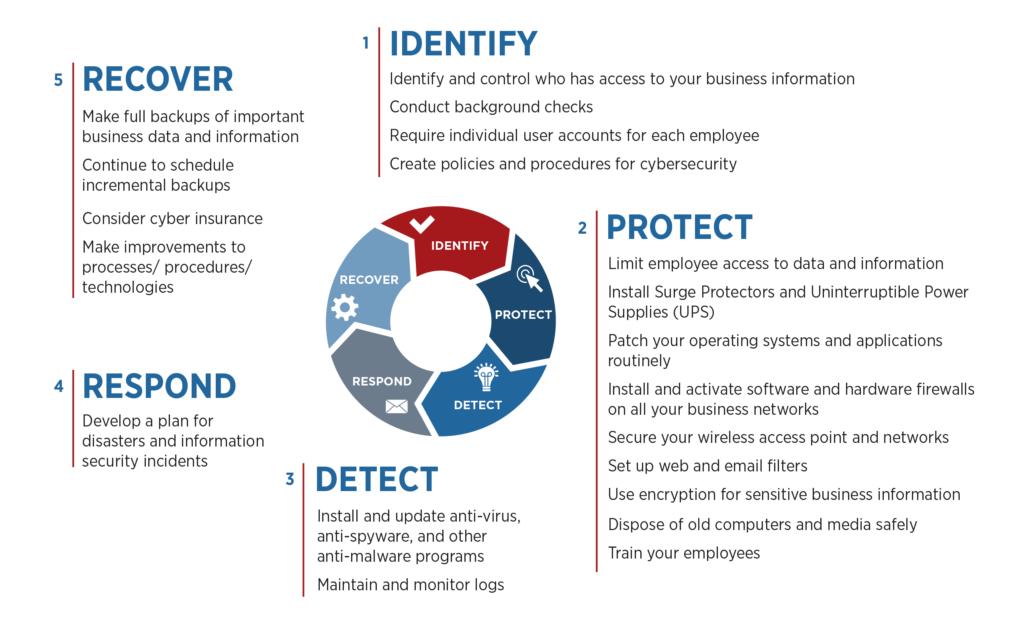
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework outlines five straightforward steps small and medium-sized manufacturers can take to protect their IP and operational technology from cybercrime:
- Identify
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
This diagram explains what each step involves:
CloudConnexa makes it easy for SMMs to quickly deploy robust, reliable network security that mitigates phishing attacks and other threats.
Phishing typically starts with an email that tricks a user into visiting what appears to be a safe website. If the user enters their login credentials on the phishing site, they’ve compromised their username and password. That site is where the login credentials or other personal data (like financial information) are obtained. OpenVPN Cloud with Cyber Shield, a built-in content filtering feature, helps curtail phishing attacks efficiently and effectively.
CloudConnexa also protects against data loss and IT infrastructure damage by giving network administrator(s) the ability to require MFA — a security measure that requires users to provide multiple forms of identity verification to access their account — without making secure access overly difficult for employees. This is especially useful with the growth of remote work.
SMMs need the ability to evolve their cybersecurity initiatives to stay ahead of threats. One way to do this is by building a baseline using reporting. The Traffic Reporting and Dashboards included with Cyber Shield delivers detailed statistics on traffic threats (malware, intrusion, DOS) as well as the device of origin.
OpenVPN is on a mission to make cloud-based cybersecurity accessible to manufacturers of all sizes. And we don’t just make it easy to get started — we also make it free. Activate your account today to see how you can quickly, easily connect private networks, devices, and servers to build a secure, virtualized modern network that meets the demands of Industry 4.0 Manufacturing.


