Access Server Simple Infrastructure Setup
Access Server supports many different network configurations. Here we outline three commonly supported network configurations for Access Server deployments. Depending on your requirements, these configurations provide good starting points to configure your VPN. After deployment, Access Server creates a VPN IP subnet for ease of routing and grants a further layer of protection for access to private networks.
Basic setup: one network interface on a private network behind a firewall
Use Access Server to set up secure access to a private network behind a firewall. This configuration includes the following:
Access Server hosted on your internal corporate network.
Users outside the network gaining access through VPN tunnels.
Access Server has one network interface to the private network.
Note
You may have other interfaces present on the system that aren't utilized by Access Server.
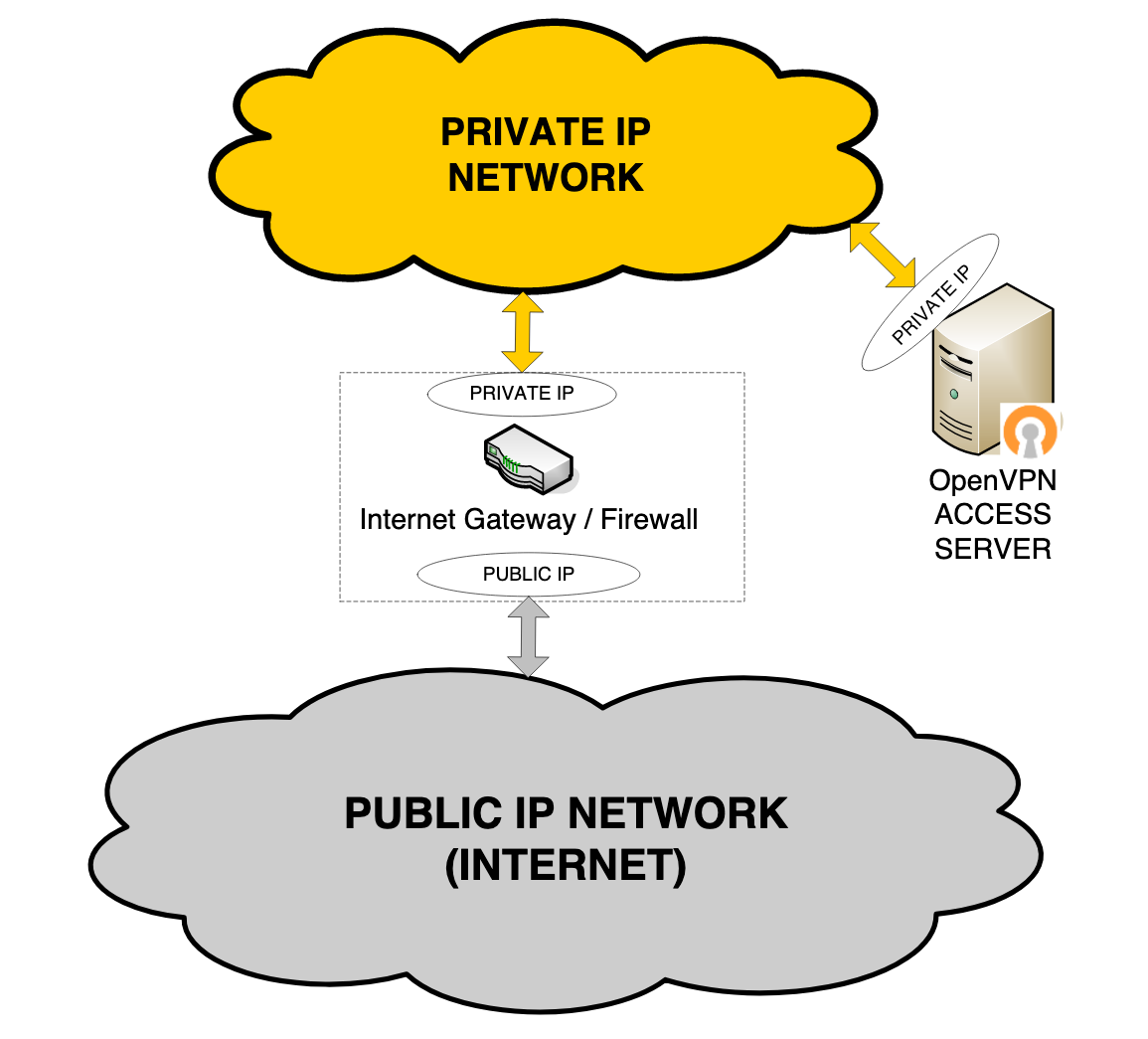
For this configuration, the internet gateway forwards TCP/UDP port traffic from the public-facing IP address to Access Server’s private IP address. At a minimum, one TCP port (typically port 443) is forwarded. That TCP port can carry both the VPN tunnel traffic and the web server/VPN client traffic. Optionally, you can separate VPN tunneling from web server traffic, in which case an additional TCP or UDP port (e.g., UDP port 1193) is forwarded for the VPN tunnel.
A variation on this network configuration has Access Server with one interface attached to a DMZ network provided by the firewall. As mentioned above, the same forwarding of client traffic is required. Additionally, you may need to configure the firewall to allow traffic between Access Server and the private network behind the firewall.