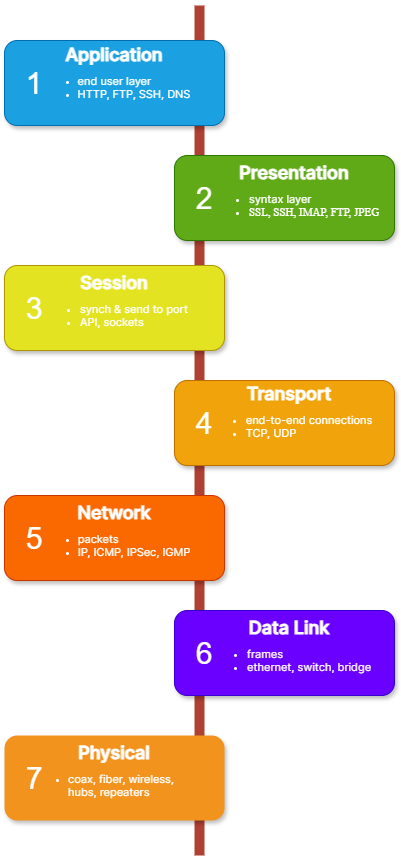
What is the OSI Model?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model represents computer network technology in seven layers. The International Organization for Standardization created the model to provide a standard for communication between computer systems. Consider the OSI model a universal language for computer networking.
Each OSI model layer performs specific tasks and communicates with the adjacent layers. Access Server operates at layer 3, also known as tunnel or routing mode. Access Server transfers TCP and UDP packets through the VPN tunnel to a target location.
Access Server layer 3 example: Access Server can send traffic from an OpenVPN client to a destination on the public internet via the OpenVPN tunnel. This works using the operating system routing table and manipulating this to send traffic through the OpenVPN virtual network adapter instead. Using the routing table, you can specify either a single IP address that traverses the VPN tunnel or a range of addresses. Thus, you can specify which IP addresses you want to use the VPN tunnel and which you don't. A simple way to think of it is Access Server works as a network router with access control on IP routing for OpenVPN clients. Each port on the router has different access rules. Think of the OpenVPN tunnels connecting the clients as virtual network cables, and Access Server allows access to a certain IP address.
If you want more information about the OSI model, read this Wikipedia article.